What is Quora ?
Quora is a social Q&A platform where users can ask and answer questions. Unlike search engines that give quick but shallow results, Quora offers more conversational, in-depth insights, often from domain experts who share their expertise.
Requirements of Quora’s Design
Functional Requirement
- Create a Space
- Question & Answer
- Ranking question based on usefulness
- Upvote
- Share
- Recommendation
- Search
Non Functional Requirement
- Highly Available
- Scalable
- Consistent
- Performance
Resource Estimation
- Total 1 billion user , 300 million active user per day
- 1 content size
- Question Text Size – 500 char – 500 * 2 = 1000 byte = 1kb
- Lets assume 10 answer, 10 comment and counters
- Total let say 100 Kb text per question
- 2 image per question = 500 kb (10% question is having image)
- 1 video – 5 mb – 5 % question is having video
- 300 million DAU ~ 300 * 100 Kb = 30000 GB = 30 TB / day Text
- 300 * 10% * 500 Kb = 15000 GB = 15 TB
- 300 * 5% * 5 Mb = 75 million Mb = 75 TB
- total let say – 115 TB / Day Storage
- 115 TB * 365 * 5 ~ 200 PB storage needed for min 5 year
- Data Bandwidth Estimation
- 1TB /Day is approx 11.6 Mbps
- 30 TB / Day = 350 Mbps
- Query Estimation
- Read Query
- Assume 10 question read per user
- 300 Million * 10 / 86400 = 3000 * 11.5 QFPS (1 Million / day ~ 11.5 QFPS) = 33K QFPS
- Write Query
- 1 person write 1 question perday
- 300 Million * 1 / 86400 = 300 * 11.5 QFPS (1 Million / day ~ 11.5 QFPS) = 3K QFPS
- Total – 36 K QFPS
- Standard Server Capacity – 64000 REQ/S Not so high
- Peak time – 300 M / 64000 = 1 Million need 16 Server * 300 = 4.8 k Server
- Read Query
Building Blocks
- Load Balancer
- Database
- Distributed Cache
- Blob Storage
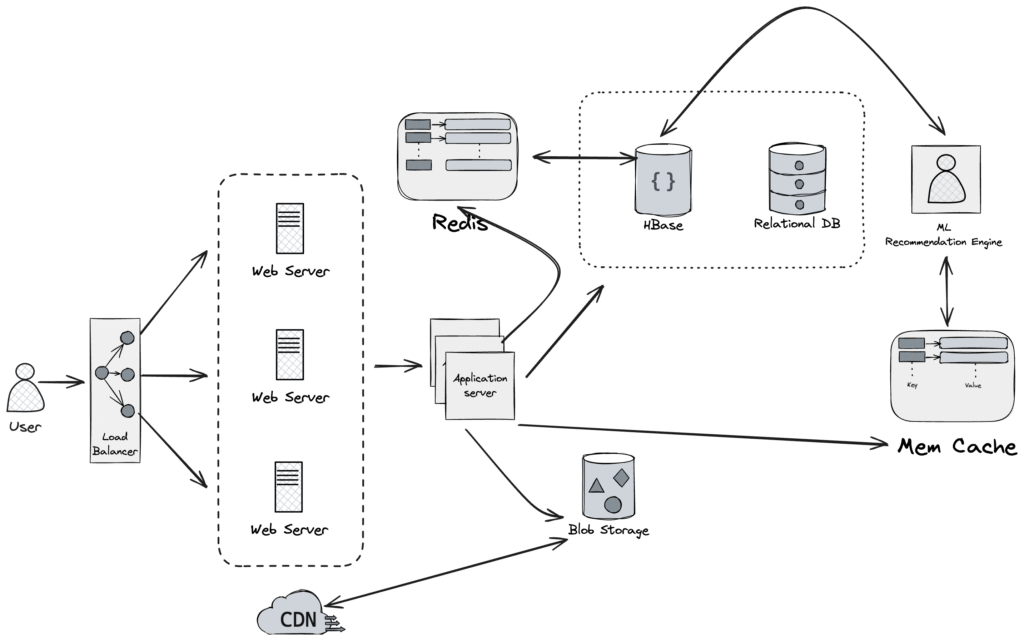
Initial Design
Database
- Relational DB (MySQL): For critical, consistent data like questions, answers, comments, and votes.
- NoSQL DB (HBase): For high-throughput storage of views, ranking scores, and extracted features (used in recommendations).
- Why HBase?
- Open-source & early availability (2008): Perfect timing for Quora’s launch in 2009.
- Based on Google BigTable: Designed for large-scale, distributed storage.
- Handles massive small-sized data: Fits Quora’s use case (views, scores, features).
- High read/write throughput: Supports parallel big data processing efficiently.
- In short: HBase was a natural early choice for Quora due to timing, scalability, and performance.
- Why HBase?
Distributed Cache
- Memcached: Caches frequently accessed critical data from MySQL.
- Redis: Stores live view counters of answers (supports fast in-store increments).
- CDN: Delivers frequently accessed videos and images efficiently.
- Multiple cache systems are used, each chosen for its strengths and specific use case.
Blob Storage
- For media files like videos and images. S3 + CDN could be right choice
Recommendation System
- Power recommendations & ranking using various attributes.
- Support both online and offline computation modes.
- Rely on ML models for effective personalization.
- Require high RAM & processing power to handle intensive workloads.
- In short: Compute servers form the backbone of Quora’s ML-driven recommendations and ranking.
Workflow
Posting Q/A/Comments):
- Request handling: User requests → Load Balancer → Web Servers → Application Servers.
- Data storage:
- Q/A stored in MySQL
- Media (videos, images) stored in Blob storage
Answer Ranking System
- Basic sort by date is easy but not user-friendly.
- Uses ML-based ranking with features stored in HBase.
- ML engine selects the most useful answer (not just most upvoted, since jokes can skew results).
- Runs mainly in offline mode → reduces infra load, captures long-term engagement.
- Needs special ML hardware → often leverages cloud elastic services.
Recommendation System
- Provides user feed, related questions, ads, respondent suggestions, duplicate/violation detection.
- Works in both online and offline modes.
- Takes features from application servers, processes via ML engine.
- Suggest user
Search Feature
- Builds index in HBase from questions, answers, topics, and usernames.
- User queries matched against the index; results refined via tokenization (handles word reordering).
- Cache serves frequently accessed indexes for low latency.
API design
- Post a question
- postQuestion(user_id, question, description, topic_label, video, image)
- Post an answer
- postAnswer(user_id, question_id, answer_text, video, image)
- Upvote or downvote a question or answer
- upvote(user_id, question_id, answer_id)
- Comment on an answer
- comment(user_id, answer_id, comment_text)
- Search
- search(user_id, search_text)
Conclusion
Quora’s design demonstrates how large-scale systems can grow with user demand. A key highlight is the use of vertical sharding in MySQL to handle scalability. The design also incorporates multiple techniques to address both functional and non-functional requirements. However, advanced features such as NLP for spelling correction and typeahead search optimizations remain outside the current scope.
Limitations and further challanges
Question & Answer Deduplication
- Challenge: Thousands of variations of the same question exist.
- Need: Detecting duplicates using NLP, clustering, and entity recognition while merging without losing context.
Moderation & Spam Control
- Challenge: Handling abusive content, fake accounts, spam links, and low-quality answers.
- Need: Scalable moderation (automated ML + human reviewers).
Content Ranking & Quality Control
- Challenge: With millions of answers, ranking the “best” one is not straightforward. Upvotes alone can be biased or gamed.
- Need: ML-based ranking systems that consider freshness, expertise, readability, and engagement.
Search at Scale
- Challenge: Users search for broad and niche questions. Query understanding is hard because natural language can be vague.
- Need: Semantic search, question deduplication (“What is AI?” vs. “Explain artificial intelligence”), and efficient indexing.